
Over the past few decades, enterprises have elected to take advantage of lower outsourcing costs abroad for their call centers. This has taken place in offices where employees can be made available for their customers even during the night hours. Nowadays, businesses have taken the next big leap in a whole new era of customer service – based in the cloud. In 2020, 39% of UK businesses had already made the translation. Now, nearly 2/3 have declared their intent to follow suit.
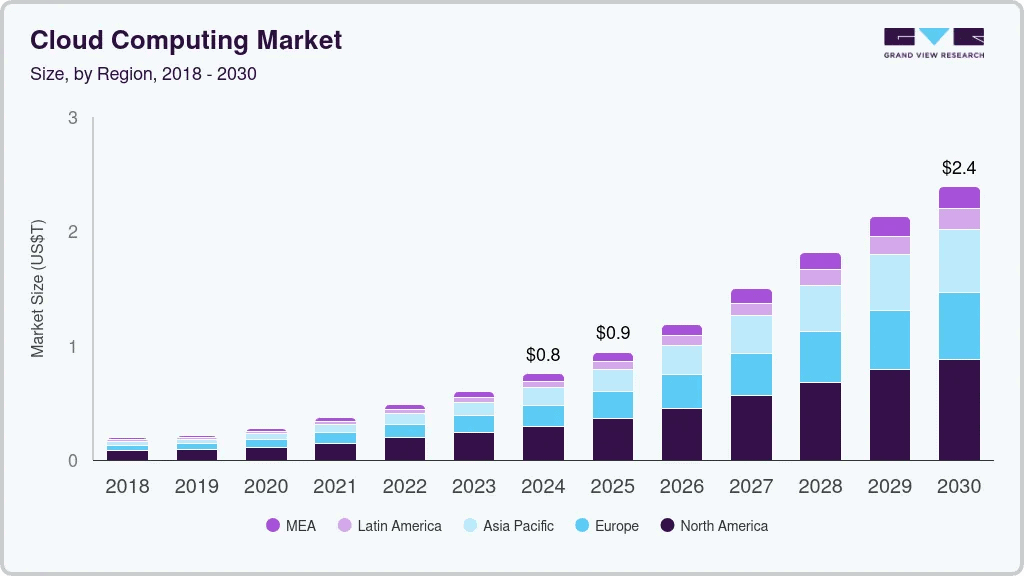
It’s no secret that superpowered computing and machine learning are all the rage right now. We’re seeing blindsiding change in many industries and jaw-dropping growth. People are now playing video games thanks to cloud infrastructure and streaming and storing their data there en masse, with cloud contact centers, just starting to blow up themselves – worth 11 billion in 2019, now in 2025 – 32.65 billion, and projected to hit 97.28 billion by 2030.
This technology is helping businesses keep customers around more, boost sales, level the playing field for smaller companies, serve governments, and, on top of all that – is a young industry undominated by major players.
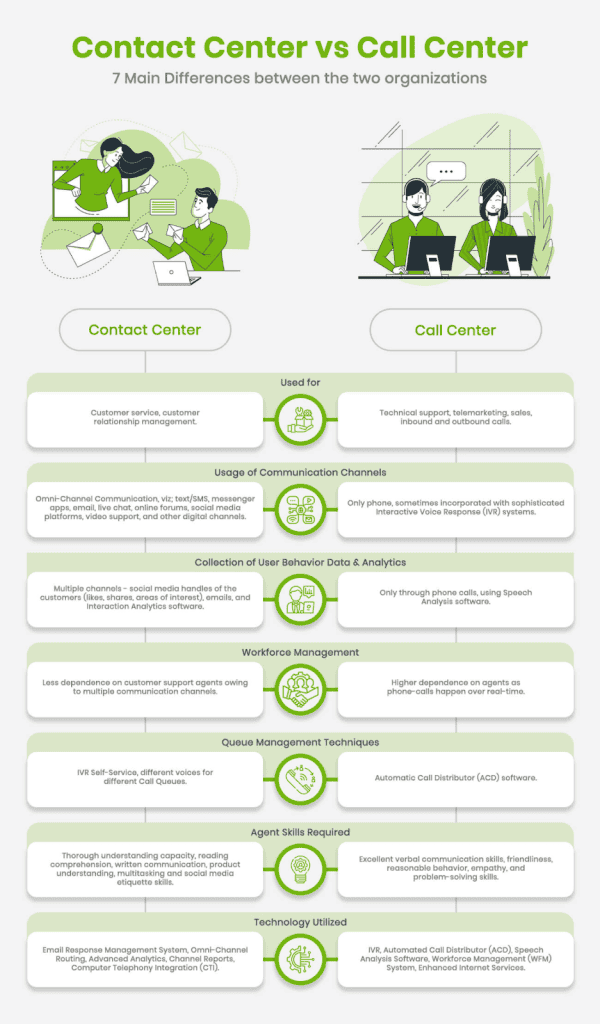
What Makes Cloud Centers So Enticing
First and foremost, running a physical call center costs a company 8$ for each customer they serve. Running it on the cloud though – a whopping 0.10 per contact. These agents work from home, negating the cost of an office, and are able to be located not only in the opposite time zone but virtually all time zones at once.
Just like CRM systems need to be combined together for keeping the team fully updated on all developments to convert sales, omnichannel support is melding all means of communication in a way that legacy equipment cannot deliver. We have also already seen a notable shift towards more and more employees getting used to working from home. 5G is a substantial step beyond 4G Internet as well, which significantly boosts the quality of conversations from both the customer’s and the live agent’s side.
Democratization of Service
In the past, the largest enterprises have enjoyed a pronounced additional edge of being able to develop their own CRM and customer care tools to reduce churn, since capital availability is not a problem for them. Now, we’re seeing more small and medium enterprises being able to access most of the same technologies through cloud call center subscription pricing. So now, even 49% of these have followed suit already, with average-size businesses resolving issues for customers 40% faster upon the first time they’re reported.
AI Enhancing Customer Lifetime Value
Voice recognition technology has gotten pretty stunning. Not only is organization totally handled thanks to self-service containment and combined channels, but these same systems are able to display words dictated to the customer in writing on the screen, rendering it easier to understand. This is true, whatever channel they contact the company from, which often is from:
- social network
- telephone
- website chatbot
- in-app
All of this unified information is further analyzed for insights, at which point the software goes on to make recommendations on ways to serve customers. It even analyzes their vocal tonality and produces reports on how on average customers are reacting to certain practices and performance. The benefit extends to displaying prompts for sales agents and customer retention ideas for disaffected customers.
AI assistants also help guide customers in the middle of a conversation. And their scale is unlimited. They are even capable of understanding slang and getting updated on new products on the market.
Foundational Technologies
The new era could not have begun if not for these essential technologies.
Interactive Voice Response
These are automated phone menu systems using pre-recorded prompts, a field which big businesses previously dominated in. Now, voice recognition is so good that dialing a button is no longer necessary. This reduces call volume for live agents and gets customers where they need faster.
Automatic Call Distribution
A routing engine receives incoming calls and distributes them to agents based on predefined rules like agent skill set, caller priority, wait time, language, or customer history. This reduces wait time and resolution time.
Computer Telephony Integration
Connects phone systems with computers and business software. When a call arrives, the system pulls relevant customer info and displays it on the agent’s screen.
Where The Growth Is Happening
Right now, there are no companies dominating the field. That said, most of the growth is surely happening in North America, where 38% of the market lies, which has one of the biggest demands to have their operations handled off-site. Following farther behind are East Asia, Southeast Asia, and India, with 15.8% CAGR. 61% of the market is also generated from big businesses.
One of the reasons the United States and Canada are such bulwarks for the industry is the 5G is very advanced and customers are more wise to budgeting for customers. A lot of people also enjoy cloud migration and many other services that cloud giants already offer. In Asia, Japan is one of the most innovative in AI, while down south, the focus is more on cost-saving and linguistic accommodation. Even the slowest-moving regions, such as Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East, are growing yearly in the double digits.
The EU, however, is the most challenging in terms of compliance and respect for customer data privacy, which is causing a leaning toward more hybrid customer care.
The biggest industry where this is happening is healthcare, followed by:
banking,
- fintech
- insurance
- IT
- telecom
- ITES
- consumer goods
- government
- tourism
- media
Concerns
One of the biggest downsides for some companies is data privacy risks, which is a net negative for cloud customer service’s growth.
Cybersecurity
Whenever a company holds its data on the Internet, this is hackers’ favorite type of target, and if a major hack does happen, that means all of the customers on that cloud could end up with their data being in the hands of criminals. In USA, 49% of people asked in one survey responded that they feel “extremely” or “very vulnerable” to a cyberattack.
However, billions are being poured into preventing that from happening. And some companies are combating that by regionalizing where they store the data, allowing customers to be the ones to hold keys, and in-depth security attestations for governments.
While the majority of deployments are public, at 42%, a third of them are private, and companies can enjoy being served in an independent center.
Migration Challenges
Due to not fully compatible legacy systems, as well as the heavy pressure states put on cloud companies, it can be technically hard to manage a full transfer to the cloud. The EU’s GDPR in particular demands complete AI transparency, which means that each automated decision must be rendered transparent. This slows down the sales process.
Especially when it comes to the most privacy-sensitive areas, these are sometimes better positioned to only maintain a hybrid of on-site and cloud infrastructure. It also does sometimes occur that a large data center can have downtimes and companies are afraid of being locked into a contract.
Competition
Right now, the biggest players in the industry own less than 35% of the market, which signals that it’s wide open and friendly to invest in. Most of these companies are distinguishing themselves based on affordable pricing, such as on a per-minute basis. The level of competition is driving prices down as well. Outfits are offering unique concentrations of AI, design for specific industries of clients, and providing quick value to customers.
