
Whether you’re logging in to your bank, social media, or favourite online store, you’ve probably seen a text message code pop up after you enter your password. This simple step is called SMS 2FA — short for SMS-based two-factor authentication. It helps protect your accounts by adding an extra layer of security that goes beyond just a password.
In this guide, you’ll see what is SMS 2FA, how it works, where it’s used, its pros and cons, and how to keep your accounts safe if you choose to use it.
What Does SMS 2FA Mean?
SMS 2FA (two-factor authentication) adds an extra step when you log in to an account. Instead of just entering your password, the website or app also sends a one-time code by text message to your phone. You must enter that code to complete the login. This extra layer makes it harder for someone to break into your account, even if they have your password.
Most people see SMS 2FA during logins to email, banking, social media, or online shopping sites. After typing your username and password, you receive a text with a short numeric code, often valid for only a few minutes. Once you enter it correctly, you gain access. This quick step helps confirm that you’re really you, and not someone who just stole or guessed your password.
Some people choose to use a virtual or temporary phone number for SMS 2FA on accounts they don’t fully trust or want to keep separate. This can add an extra layer of privacy, but it’s important to make sure you can still access that number when you need it.
Popular temporary SMS platforms include Receive-sms.io, Receive-SMS-Online.info, and FreePhoneNum.com. These services can help you receive one-time verification codes without sharing your real number. Just remember that some free numbers are shared or recycled, so use them only for accounts you’re willing to lose if the number stops working.
How SMS 2FA Works Step-by-Step
- Enter your username or email
Go to the login page of the site or app you want to access. - Type your password
This is your first layer of security — make sure it’s strong and unique. - Receive a one-time code by SMS
The site sends a short numeric or alphanumeric code to the phone number linked to your account. - Check your text messages
Open your messaging app to find the code.
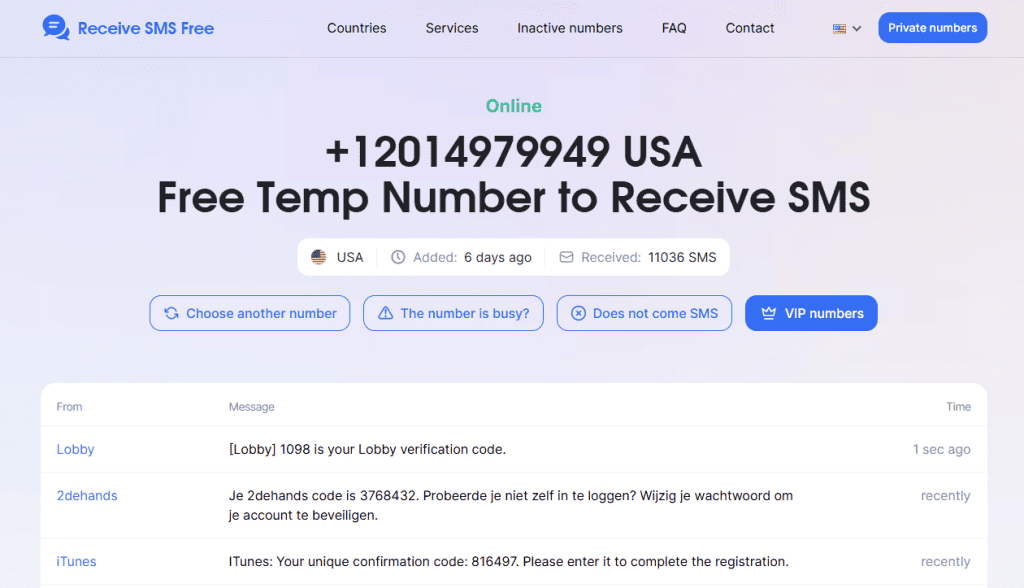
- Enter the code on the website or app
Type the code in the 2FA field. This step confirms you have access to that phone number. - Access granted
If the code is correct, you’re logged in. If not, you won’t be able to continue, keeping your account safer from intruders.
Common Use Cases for SMS 2FA
- Online banking
Banks and financial apps use SMS 2FA to verify your identity during logins, money transfers, or when adding new payees. - Social media accounts
Sites like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter rely on SMS 2FA to protect accounts from hijacking. - E-commerce sites
Online stores, payment processors, and marketplaces often require SMS codes to confirm large purchases or password changes. - Email services
Providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook may send a text code when you log in from an unrecognized device. - Cloud storage services
Dropbox, Google Drive, and similar platforms use SMS 2FA to keep your files safe if someone steals your main password. - Workplace accounts
Many companies use SMS 2FA for employee logins to VPNs, work dashboards, or collaboration tools. - Crypto exchanges and trading platforms
Exchanges often use SMS 2FA to secure logins and withdrawals, though many recommend using an authenticator app instead.
How Secure Is SMS 2FA?
| Strengths | Vulnerabilities |
| Easy to set up — works on any phone with SMS capability | SIM swapping: attackers trick your carrier into giving them your number |
| No need for extra apps or devices | SMS messages can be intercepted over insecure networks |
| Better than just a password alone | Malware on your phone could steal text messages |
| Universally supported by banks, apps, and sites | Delays or failure to receive codes in low-signal areas |
| Good fallback when authenticator apps or hardware keys aren’t available | Losing access to a temporary or virtual number used for 2FA |
| A familiar process that most people already know how to use | Numbers recycled by carriers may let strangers receive your SMS codes |
| Useful for basic personal accounts that don’t store sensitive data | Not recommended for high-value accounts where stronger 2FA is available |
SMS 2FA vs. Other 2FA Methods
Comparison with authenticator apps
Authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) that don’t rely on your phone number or carrier network. This means hackers can’t use SIM swapping or SMS interception to break in. Authenticator apps are more secure for accounts you can’t afford to lose, like banking, crypto wallets, or work systems. However, they can be less convenient since you need to install and back up the app.
Hardware keys and push notifications
Physical security keys (like YubiKey or Titan) are one of the strongest 2FA options. They require an attacker to possess the device to get in physically, so stealing your password alone is useless. Push notifications (like those from Duo or Okta) work by sending a prompt to your phone to approve or deny a login. These are more secure than SMS, but they still rely on you having your phone and internet access.
Temp vs. Permanent Numbers for 2FA
Using a temporary or virtual number for 2FA can add privacy because you don’t reveal your real personal number to every site. This is useful for testing services, signing up for trials, or keeping spam away. However, it has risks:
- If you lose access to your temp or virtual number, you could get locked out permanently.
- Some services block known disposable numbers or virtual ranges.
- For accounts that really matter — like banking, crypto, or work accounts — a stable, secure number you always control is safer.
- For disposable or less critical accounts, a temporary number is sufficient if you maintain backups and recovery methods.
Best Practices When Using SMS 2FA
- Keep your phone number safe
Don’t post it publicly or share it with sites you don’t trust. If your carrier offers PIN protection for your SIM, enable it to help prevent SIM swapping. - Consider a temporary number for non-critical accounts
Use a temporary or virtual number when signing up for sites you want to test or when you want extra privacy. Just remember, you may lose access if you stop paying for the virtual number or the service recycles it. - Avoid public disposable SMS sites for sensitive accounts
Never use free, public SMS sites to receive 2FA codes for accounts that store important information or money. Public numbers are shared so that anyone can see your messages. - Use backup codes
Many sites let you generate backup codes when you turn on 2FA. Store these safely (like in a password manager) so you can get back into your account if you lose your phone or number. - Combine with strong passwords
2FA is pointless if your password is weak or reused across multiple sites. Use a unique, strong password for each account, and store them in a reputable password manager. - Add an authenticator app or hardware key for extra protection
If the service supports multiple 2FA methods, add an authenticator app or security key. These options protect you from the most common SMS attacks like SIM swaps and phishing.
Key Takeaways
SMS 2FA adds an extra step to keep your accounts safer than using just a password. For more privacy, consider using a temporary or virtual number on less critical sites. Just be careful not to lose access, or you could get locked out.
Always back up with recovery codes or an authenticator app, and use strong, unique passwords. For sensitive accounts, consider stronger options like hardware keys.
Keep your phone number secure, stay alert for SIM swap scams, and choose the right method for each account to protect both your security and privacy.
